Protein / Amino acid review
Nine Essential amino acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and therefore it is 'essential' to include them in the diet.
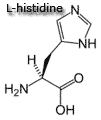
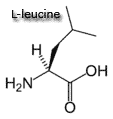
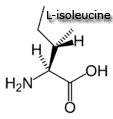
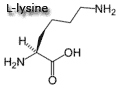
histidine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine.
Estimated daily requirements for an adult based on the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-essential amino acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
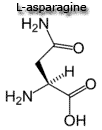
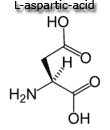
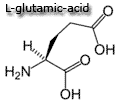
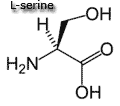
| Generally, these amino acids are considered non-essential because they can be synthesized from other amino acids.
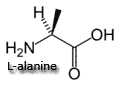
alanine,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conditional amino acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
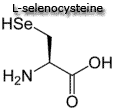
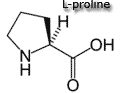
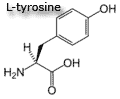
| Conditionally essential amino acids are usually not required in the diet, however, some individuals do not synthesize some of these amino acids in sufficient amounts and therefore must be included in the diet. An example would be a patient with phenylketonuria who must drastically restrict phenylalanine intake in order to prevent severe metabolic disturbances. The reduction in the available phenylalanine causes a profound reduction in tyrosine production which is normally synthesized by the conversion of phenylalanine. Therefore tyrosine becomes an essential amino acid.
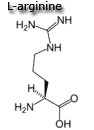
arginine,
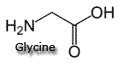
Note: glycine is the simplest amino acid. Note its basic structure..... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Special cases - Sulfur-containing amino acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sulfur-containing amino acids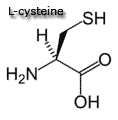  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
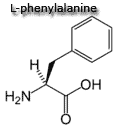
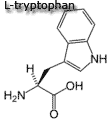
Special cases - Aromatic amino acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aromatic amino acids - Each of these amino acids contain a ring structure.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Special cases - Branched Chain Amino Acids |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
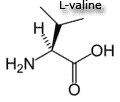
| Branched-chain Amino Acids: leucine, isoleucine and valine
The branched chain amino acids (BCAA) are all essential. Each BCAA has a bulky nonpolar aliphatic side chain (open-chain hydrocarbon - carbon atom bound to more than two other carbon atoms). Other:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Several of these calculators may be particularly useful for dieters. Just about every single MAJOR calorie/ energy equation that has been released over the last 90 years is included below. Each calculator has a customized printout option for easy analysis. Recommendation: Try each calculator - print out the results - then compare!
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) Overview.
- Harris-Benedict Equation: Estimation of total calories needed. MOST widely used equation for calculating basal metabolic rate and total calories.
- Revised Harris-Benedict Equation:The original Harris Benedict equation was revised in 1984. This updated equation can be used to calculate the basal metabolic rate and total calories.
- RESTING Metabolic Rate (RMR): Resting Metabolic Rate Calc - This equation can be used to calculate the RESTING metabolic rate and total calories. Mifflin-St Jeor equation.
- Schofield equation (BMR) : This equation was part of the previous government guidelines to formulate RDA's and can be used to calculate the basal metabolic rate and total calories needed.
- Institute of Medicine Equation- LATEST EQUATION: IOM Equation-Estimated Energy Requirement (EER) Estimation of total calories needed. This equation is behind the 2005 Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the new food pyramid, MyPyramid.
- Energy Requirements in ICU patients - Ireton-Jones
- Check out the new BMR multi-calc
 .
.
Body Weight Calculators
- Adjusted Body Weight Calculator and Ideal Body Weight Calculator
- Body Mass Index Calculator - BMI - Determines if your weight is in proportion to your height based on Federal guidelines released by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The BMI is helpful in determining health risks and appropriate interventions.
- Dieting Calculator - This calculator provides several useful outputs including the calculated 'Body Mass Index' or BMI. It will also estimate your 'Basal Metabolic Rate' or BMR. Also included is an estimate of your 'Total Energy Expenditure' or TEE which indicates the number of calories needed per day to maintain your current weight.
Fiber Calculators
- Soluble Fiber Calculator - Cholesterol lowering
 - Soluble fiber: viscous fiber that delays gastric emptying and can result in an extended feeling of fullness. Need at least 7 grams per day to maximize cholesterol lowering benefits.
- Soluble fiber: viscous fiber that delays gastric emptying and can result in an extended feeling of fullness. Need at least 7 grams per day to maximize cholesterol lowering benefits. - TOTAL Fiber Calculator - Great tool for dieters! - Insoluble fiber: does not dissolve in water and is not affected by digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. Insoluble fiber provides bulk which eases defecation.
- Daily Fiber Requirements based on AGE
Protein
- Protein requirements (daily) - calculate the amount of protein that should be consumed daily based on the latest guidelines.


- Protein - Amino Acid Review - Essential, non-essential, conditional, branched chains...
- Essential Amino Acid Calculator - What are the recommendations?
- Protein sources (Plant-based versus animal source)
Other Diet and Nutrition Calculators