Typical reductions in A1C values - DPP-4 INHIBITORS:
~ 0.74% (0.73 - 1.2)
Background
Overview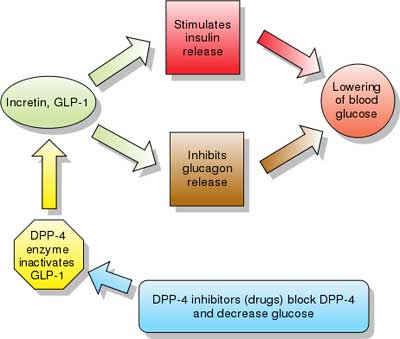 |
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE NESINA is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Limitation of Use: Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION •The recommended dose in patients with normal renal function or mild renal impairment is 25 mg once daily.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS |
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE: TRADJENTA is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Important limitations of use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: ADVERSE REACTIONS: To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or 1-800-459-9906 TTY, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS: USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Pharmacodynamics: Cardiac Electrophysiology: Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: |
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE: ONGLYZA is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in multiple clinical settings. (Monotherapy and Combination Therapy) Important limitations of use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Other: ----------------------------------------- The dose of ONGLYZA is 2.5 mg once daily for patients with moderate or severe renal impairment, or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis (creatinine clearance [CrCl] ≤50 mL/min). ONGLYZA should be administered following hemodialysis. ONGLYZA has not been studied in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Assess renal function prior to initiation of ONGLYZA and periodically thereafter. Creatinine clearance was estimated from serum creatinine based on the Cockcroft-Gault formula: [ 2 ] Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Combination product: Saxagliptin and Metformin (Kombiglyze™ XR) CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: ADVERSE REACTIONS: 2] Peripheral edema was reported more commonly in patients treated with the combination of ONGLYZA and a thiazolidinedione (TZD) than in patients treated with the combination of placebo and TZD. 3] Hypoglycemia was reported more commonly in patients treated with the combination of ONGLYZA and sulfonylurea than in patients treated with the combination of placebo and sulfonylurea. 4] Hypersensitivity-related events (e.g., urticaria, facial edema) were reported more commonly in patients treated with ONGLYZA than in patients treated with placebo. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-800-721-5072 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS: USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: 2] Safety and effectiveness of ONGLYZA in pediatric patients below the age of 18 have not been established. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacodynamics: Cardiac Electrophysiology: Pharmacokinetics: No appreciable accumulation of either saxagliptin or its active metabolite was observed with repeated once-daily dosing at any dose level. No dose- and time-dependence were observed in the clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite over 14 days of once-daily dosing with saxagliptin at doses ranging from 2.5 to 400 mg. Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: Excretion: |
| These highlights do not include all the information needed to use JANUVIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for JANUVIA.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Important Limitations of Use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Patients with Renal Insufficiency: For patients with mild renal insufficiency: (creatinine clearance [CrCl] ≥50 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of ≤1.7 mg/dL in men and ≤1.5 mg/dL in women), no dosage adjustment for JANUVIA is required. For patients with moderate renal insufficiency: (CrCl ≥30 to <50 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of >1.7 to ≤3.0 mg/dL in men and >1.5 to ≤2.5 mg/dL in women), the dose of JANUVIA is 50 mg once daily. For patients with severe renal insufficiency: (CrCl <30 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of >3.0 mg/dL in men and >2.5 mg/dL in women) or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, the dose of JANUVIA is 25 mg once daily. JANUVIA may be administered without regard to the timing of hemodialysis. Because there is a need for dosage adjustment based upon renal function, assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiation of JANUVIA and periodically thereafter. Creatinine clearance can be estimated from serum creatinine using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. There have been postmarketing reports of worsening renal function in patients with renal insufficiency, some of whom were prescribed inappropriate doses of sitagliptin. Cockcroft-Gault formula: Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or with Insulin: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: There have been postmarketing reports of acute renal failure, sometimes requiring dialysis. Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency and in patients with ESRD. Assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiating JANUVIA and periodically thereafter. There is an increased risk of hypoglycemia when JANUVIA is added to an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin therapy. Consider lowering the dose of the sulfonylurea or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. There have been postmarketing reports of serious allergic and hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with JANUVIA such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome. In such cases, promptly stop JANUVIA, assess for other potential causes, institute appropriate monitoring and treatment, and initiate alternative treatment for diabetes. There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with JANUVIA or any other anti-diabetic drug. ADVERSE REACTIONS: To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Safety and effectiveness of JANUVIA in children under 18 years have not been established. (8.4) CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacodynamics: In a two-day study in healthy subjects, sitagliptin alone increased active GLP-1 concentrations, whereas metformin alone increased active and total GLP-1 concentrations to similar extents. Co-administration of sitagliptin and metformin had an additive effect on active GLP-1 concentrations. Sitagliptin, but not metformin, increased active GIP concentrations. It is unclear how these findings relate to changes in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. In studies with healthy subjects, JANUVIA did not lower blood glucose or cause hypoglycemia. Cardiac Electrophysiology: In patients with type 2 diabetes administered JANUVIA 100 mg (N=81) or JANUVIA 200 mg (N=63) daily, there were no meaningful changes in QTc interval based on ECG data obtained at the time of expected peak plasma concentration. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: The absolute bioavailability of sitagliptin is approximately 87%. Because coadministration of a high-fat meal with JANUVIA had no effect on the pharmacokinetics, JANUVIA may be administered with or without food. Distribution: The mean volume of distribution at steady state following a single 100 mg intravenous dose of sitagliptin to healthy subjects is approximately 198 liters. The fraction of sitagliptin reversibly bound to plasma proteins is low (38%). Metabolism: Approximately 79% of sitagliptin is excreted unchanged in the urine with metabolism being a minor pathway of elimination. Following a [14C]sitagliptin oral dose, approximately 16% of the radioactivity was excreted as metabolites of sitagliptin. Six metabolites were detected at trace levels and are not expected to contribute to the plasma DPP-4 inhibitory activity of sitagliptin. In vitro studies indicated that the primary enzyme responsible for the limited metabolism of sitagliptin was CYP3A4, with contribution from CYP2C8. Excretion: Following administration of an oral [14C]sitagliptin dose to healthy subjects, approximately 100% of the administered radioactivity was eliminated in feces (13%) or urine (87%) within one week of dosing. The apparent terminal t1/2 following a 100 mg oral dose of sitagliptin was approximately 12.4 hours and renal clearance was approximately 350 mL/min. Elimination of sitagliptin occurs primarily via renal excretion and involves active tubular secretion. Sitagliptin is a substrate for human organic anion transporter-3 (hOAT-3), which may be involved in the renal elimination of sitagliptin. The clinical relevance of hOAT-3 in sitagliptin transport has not been established. Sitagliptin is also a substrate of p-glycoprotein, which may also be involved in mediating the renal elimination of sitagliptin. However, cyclosporine, a p-glycoprotein inhibitor, did not reduce the renal clearance of sitagliptin. |
| These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KOMBIGLYZE XR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KOMBIGLYZE XR.
KOMBIGLYZE XR (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors: No studies have been performed specifically examining the safety and efficacy of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients previously treated with other antihyperglycemic medications and switched to KOMBIGLYZE XR. Any change in therapy of type 2 diabetes should be undertaken with care and appropriate monitoring as changes in glycemic control can occur. Inform patients that KOMBIGLYZE XR tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed, cut, or chewed. Occasionally, the inactive ingredients of KOMBIGLYZE XR will be eliminated in the feces as a soft, hydrated mass that may resemble the original tablet. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: Vitamin B12 deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B12 levels. Measure hematological parameters annually. Hypoglycemia: When used with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea), a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Macrovascular outcomes: No conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with KOMBIGLYZE XR or any other antidiabetic drug. ADVERSE REACTIONS: Adverse reactions reported in ≥55% of patients treated with saxagliptin and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo are: upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and headache. Adverse reactions reported in ≥55% of treatment-naive patients treated with coadministered saxagliptin and metformin and more commonly than in patients treated with metformin alone are: headache and nasopharyngitis. Hypersensitivity-related events (e.g., urticaria, facial edema) were reported more commonly in patients treated with saxagliptin than in patients treated with placebo. |
| These highlights do not include all the information needed to use JANUMET safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for JANUMET.
Initial U.S. Approval: 2007 WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Important Limitations of Use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: May adjust the dosing based on effectiveness and tolerability while not exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of 100 mg sitagliptin and 2000 mg metformin. JANUMET should be given twice daily with meals, with gradual dose escalation, to reduce the gastrointestinal (GI) side effects due to metformin. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma. History of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to JANUMET or sitagliptin (one of the components of JANUMET), such as anaphylaxis or angioedema. Temporarily discontinue JANUMET in patients undergoing radiologic studies involving intravascular administration of iodinated contrast materials. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: There have been postmarketing reports of acute renal failure, sometimes requiring dialysis. Before initiating JANUMET and at least annually thereafter, assess renal function and verify as normal. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue JANUMET. Measure hematologic parameters annually. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake. May need to discontinue JANUMET and temporarily use insulin during periods of stress and decreased intake of fluids and food as may occur with fever, trauma, infection or surgery. Promptly evaluate patients previously controlled on JANUMET who develop laboratory abnormalities or clinical illness for evidence of ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis. When used with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or with insulin, a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. There have been postmarketing reports of serious allergic and hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with sitagliptin (one of the components of JANUMET), such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome. In such cases, promptly stop JANUMET, assess for other potential causes, institute appropriate monitoring and treatment, and initiate alternative treatment for diabetes. There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with JANUMET or any other anti-diabetic drug. ADVERSE REACTIONS: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients treated with sitagliptin in combination with sulfonylurea and metformin and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo in combination with sulfonylurea and metformin were hypoglycemia and headache. Hypoglycemia was the only adverse reaction reported in ≥5% of patients treated with sitagliptin in combination with insulin and metformin and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo in combination with insulin and metformin. Nasopharyngitis was the only adverse reaction reported in ≥5% of patients treated with sitagliptin monotherapy and more commonly than in patients given placebo. The most common (>5%) adverse reactions due to initiation of metformin therapy are diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, flatulence, abdominal discomfort, indigestion, asthenia, and headache. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS: USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. To report drug exposure during pregnancy call 1-800-986-8999. |
| Drug: JANUMET ® XR (sitagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) [Drug information / PDF] Dosing: Click (+) next to Dosage and Administration section (drug info link) ABBREVIATED MONOGRAPH - SEE PACKAGE INSERT. Initial U.S. Approval: 2012 Mechanism of Action: JANUMET XR JANUMET XR tablets combine two antidiabetic medications with complementary mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes: sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, and metformin hydrochloride extended-release, a member of the biguanide class. Sitagliptin Metformin hydrochloride INDICATIONS AND USAGE Important Limitations of Use: DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS CONTRAINDICATIONS WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Temporarily discontinue JANUMET XR in patients undergoing radiologic studies with intravascular administration of iodinated contrast materials or any surgical procedures necessitating restricted intake of food or fluids. (5.1, 5.4, 5.7, 5.11) There have been postmarketing reports of acute renal failure in patients treated with sitagliptin with or without metformin, sometimes requiring dialysis. Before initiating JANUMET XR and at least annually thereafter, assess renal function and verify as normal. (4, 5.1, 5.4, 5.10, 6.2) Vitamin B12 deficiency: Metformin may lower Vitamin B12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters annually. (5.5, 6.1) When used with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or with insulin, a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia. (2.1, 5.9) Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking DPP-4 inhibitors. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate. (5.15) There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with JANUMET XR or any other anti-diabetic drug. (5.16) |
| Drug UPDATES: JENTADUETO® XR (linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride ER) tablets [Drug information / PDF] Package insert - Dosing: Click (+) next to Dosage and Administration section (drug info link) BOXED WARNING: Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., cationic drugs such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment. Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the full prescribing information [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)]. If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue JENTADUETO XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Initial U.S. Approval: 2016 Mechanism of Action: Linagliptin Metformin INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Important limitations of use: Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis (1.2) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: HOW SUPPLIED: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors: Their mechanism of action is thought to result from increased incretin levels (GLP-1 and GIP) by inhibiting its degradation by dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Increased incretin levels inhibit glucagon release, which in turn increases insulin secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases blood glucose levels.
"In one RCT comprising 206 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HgbA1c of 7.8%) receiving either 50 or 100 mg/d of Sitagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.7% (combined result of both doses). A combined result of 5 RCTs enlisting a total of 279 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HbA1c of 8%) receiving 5 mg/d of Saxagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.73%. A combined result of 5 RCTs enlisting a total of 238 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HbA1c of 8.6%) receiving 100 mg/d of Vildagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 1.2%. Another set of 6 combined RCTs involving Alogliptin (not yet approved, might be released in 2012) was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.73% in 455 patients aged 65 or older who received 12.5 or 25 mg/d of the medication." [source] DPP-4 inhibitors lowered hemoglobin A1C values by 0.74%, comparable to other anti-diabetic drugs. The first agent of the class - sitagliptin - was approved by the FDA in 2006. Examples - Drugs belonging to this class are : 1. sitagliptin (FDA approved 2006, marketed by Merck & Co. as Januvia), Berberine, the common herbal dietary supplement, too inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase-4, which at least partly explains its antihyperglycemic activity. Risks and side effects: Although extensive long-term, preclinical studies of the major DPP-4 inhibitors have failed to show any evidence of potential to cause tumors in laboratory animals, one in vitro study has raised some questions. [source] |
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine, DailyMed Database.
Provides access to the latest drug monographs submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Please review the latest applicable package insert for additional information and possible updates. A local search option of this data can be found here.