Testosterone products
Androderm® (testosterone transdermal system)
| ANDRODERM® (testosterone transdermal system), for topical use CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1995 INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) Important limitations of use: Safety and efficacy of ANDRODERM in males less than 18 years old have not been established. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: To ensure proper dosing, approximately 2 weeks after starting therapy, the early morning serum testosterone concentration should be measured following system application in the previous evening. Serum testosterone concentrations measured in the early morning outside the range of 400 - 930 ng/dL require increasing the daily dose to 6 mg (i.e., one 4 mg/day and one 2 mg/day system) or decreasing the daily dose to 2 mg (i.e., one 2 mg/day system), maintaining nightly application. Patients currently maintained on ANDRODERM 2.5 mg/day systems applied once daily may be switched to ANDRODERM 2 mg/day systems applied once daily in the evening at the next scheduled dose. Patients currently maintained on ANDRODERM 5 mg/day systems applied once daily may be switched to ANDRODERM 4 mg/day systems applied once daily in the evening at the next scheduled dose. Patients currently maintained on ANDRODERM 7.5 mg (2.5 mg/day and 5 mg/day systems) applied once daily may be switched to ANDRODERM 6 mg (2 mg/day and 4 mg/day systems) applied once daily in the evening at the next scheduled dose. To ensure proper dosing, approximately 2 weeks after switching therapy an early morning serum testosterone concentration should be measured following system application the previous evening. CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS: To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Watson Laboratories, Inc. at 1-800-272-5525 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: Review PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: SOURCE: |
Androgel® (testosterone gel) 1%
| AndroGel® (testosterone gel) 1% for topical use CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1953
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Important limitations of use:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS::
ADVERSE REACTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS:
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: Review PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Metered-dose pump that delivers 12.5 mg of testosterone per actuation. SOURCE: |
Androgel® (testosterone gel) 1.62%
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE: AndroGel 1.62% is an androgen indicated for replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone: 1] Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH], luteinizing hormone [LH]) above the normal range. 2] Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): idiopathic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations, but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range. Important limitations of use: Safety and efficacy of AndroGel 1.62% in males < 18 years old have not been established DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: The dose can be adjusted between a minimum of 20.25 mg of testosterone (1 pump actuation) and a maximum of 81 mg of testosterone (4 pump actuations). To ensure proper dosing, the dose should be titrated based on the pre-dose morning serum testosterone concentration from a single blood draw at approximately 14 days and 28 days after starting treatment or following dose adjustment. In addition, serum testosterone concentration should be assessed periodically thereafter. Table 1 describes the dose adjustments required at each titration step. Table 1: Dose Adjustment Criteria
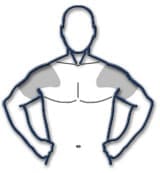
The application site and dose of AndroGel 1.62% are not interchangeable with other topical testosterone products. Table 2: Application Sites for AndroGel 1.62%
The prescribed daily dose of AndroGel 1.62% should be applied to the right and left upper arms and shoulders as shown in the shaded areas in Figure 1. Once the application site is dry, the site should be covered with clothing [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY]. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid fire, flames or smoking until the gel has dried since alcohol based products, including AndroGel 1.62%, are flammable. The patient should avoid swimming or showering or washing the administration site for a minimum of 2 hours after application [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY]. To obtain a full first dose, it is necessary to prime the canister pump. To do so, with the canister in the upright position, slowly and fully depress the (actuator) three times. Safely discard the gel from the first three actuations. It is only necessary to prime the pump before the first dose. After the priming procedure, fully depress the actuator once for every 20.25 mg of AndroGel 1.62%. AndroGel 1.62% should be delivered directly into the palm of the hand and then applied to the application sites. Alternatively, AndroGel 1.62% can be applied directly to the application sites. Strict adherence to the following precautions is advised in order to minimize the potential for secondary exposure to testosterone from AndroGel 1.62%-treated skin:
CONTRAINDICATIONS: AndroGel 1.62% may cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. Exposure of a fetus or nursing infant to androgens may result in varying degrees of virilization. Pregnant women or those who may become pregnant need to be aware of the potential for transfer of testosterone from men treated with AndroGel 1.62%. If a pregnant woman is exposed to AndroGel 1.62%, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see package insert for WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and Use In Specific Populations]. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: AndroGel 1.62% is supplied in a metered-dose pump that delivers 20.25 mg of testosterone per complete pump actuation. The pump is composed of plastic and stainless steel and an LDPE/aluminum foil inner liner encased in rigid plastic with a polypropylene cap. The metered-dose pump is capable of dispensing 60 metered pump actuations. One pump actuation delivers 1.25 g of gel. SOURCE: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Axiron® (testosterone) topical solution
| AXIRON (testosterone) topical solution, for topical use CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1953
INDICATIONS AND USAGE: 1] Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) Important limitations of use: Safety and efficacy of AXIRON in males <18 years old have not been established DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
ADVERSE REACTIONS: To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS:
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: SOURCE: |
Aveed® (testosterone undecanoate) injection
| Drug UPDATES: AVEED® (testosterone undecanoate) injection, for intramuscular use - CIII Initial U.S. Approval: 1953 [Drug information / PDF] Dosing: Click (+) next to Dosage and Administration section (drug info link) U.S. Approval: 2014. Mechanism of Action: Endogenous androgens, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) are responsible for the normal growth and development of the male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects include the growth and maturation of prostate, seminal vesicles, penis, and scrotum; the development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest, and axillary hair; laryngeal enlargement, vocal cord thickening, and alterations in body musculature and fat distribution. Male hypogonadism, a clinical syndrome resulting from insufficient secretion of testosterone, has two main etiologies. Primary hypogonadism is caused by defects of the gonads, such as Klinefelter’s syndrome or Leydig cell aplasia, whereas secondary hypogonadism is the failure of the hypothalamus (or pituitary) to produce sufficient gonadotropins (FSH, LH). INDICATIONS AND USAGE: o Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) Aveed should only be used in patients who require testosterone replacement therapy and in whom the benefits of the product outweigh the serious risks of pulmonary oil microembolism and anaphylaxis (1). Limitations of use: HOW SUPPLIED: 750 mg/3 mL (250 mg/mL) testosterone undecanoate sterile injectable solution is provided in an amber glass, single use vial with silver-colored crimp seal and gray plastic cap |
Delatestryl® (testosterone enanthate) injection
| DESCRIPTION DELATESTRYL® (Testosterone Enanthate Injection, USP) provides testosterone enanthate, a derivative of the primary endogenous androgen testosterone, for intramuscular administration. In their active form, androgens have a 17-beta-hydroxy group. Esterification of the 17-beta-hydroxy group increases the duration of action of testosterone; hydrolysis to free testosterone occurs in vivo. Each mL of sterile, colorless to pale yellow solution provides 200 mg testosterone enanthate in sesame oil with 5 mg chlorobutanol (chloral derivative) as a preservative. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Androgens also cause retention of nitrogen, sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, and decreased urinary excretion of calcium. Androgens have been reported to increase protein anabolism and decrease protein catabolism. Nitrogen balance is improved only when there is sufficient intake of calories and protein. Androgens are responsible for the growth spurt of adolescence and for the eventual termination of linear growth which is brought about by fusion of the epiphyseal growth centers. In children, exogenous androgens accelerate linear growth rates but may cause a disproportionate advancement in bone maturation. Use over long periods may result in fusion of the epiphyseal growth centers and termination of the growth process. Androgens have been reported to stimulate the production of red blood cells by enhancing the production of erythropoietic stimulating factor. During exogenous administration of androgens, endogenous testosterone release is inhibited through feedback inhibition of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH). At large doses of exogenous androgens, spermatogenesis may also be suppressed through feedback inhibition of pituitary follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). There is a lack of substantial evidence that androgens are effective in fractures, surgery, convalescence, and functional uterine bleeding. Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - Testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, or orchidectomy. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - Idiopathic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency, or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. (Appropriate adrenal cortical and thyroid hormone replacement therapy are still necessary, however, and are actually of primary importance.) If the above conditions occur prior to puberty, androgen replacement therapy will be needed during the adolescent years for development of secondary sexual characteristics. Prolonged androgen treatment will be required to maintain sexual characteristics in these and other males who develop testosterone deficiency after puberty. Delayed puberty - DELATESTRYL® (Testosterone Enanthate Injection, USP) may be used to stimulate puberty in carefully selected males with clearly delayed puberty. These patients usually have a familial pattern of delayed puberty that is not secondary to a pathological disorder; puberty is expected to occur spontaneously at a relatively late date. Brief treatment with conservative doses may occasionally be justified in these patients if they do not respond to psychological support. The potential adverse effect on bone maturation should be discussed with the patient and parents prior to androgen administration. An X-ray of the hand and wrist to determine bone age should be obtained every six months to assess the effect of treatment on the epiphyseal centers (see WARNINGS). Females In general, total doses above 400 mg per month are not required because of the prolonged action of the preparation. Injections more frequently than every two weeks are rarely indicated. NOTE: Use of a wet needle or wet syringe may cause the solution to become cloudy; however this does not affect the potency of the material. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. DELATESTRYL is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Male hypogonadism: As replacement therapy, i.e., for eunuchism, the suggested dosage is 50 to 400 mg every 2 to 4 weeks. In males with delayed puberty: Various dosage regimens have been used; some call for lower dosages initially with gradual increases as puberty progresses, with or without a decrease to maintenance levels. Other regimens call for higher dosage to induce pubertal changes and lower dosage for maintenance after puberty. The chronological and skeletal ages must be taken into consideration, both in determining the initial dose and in adjusting the dose. Dosage is within the range of 50 to 200 mg every 2 to 4 weeks for a limited duration, for example, 4 to 6 months. X-rays should be taken at appropriate intervals to determine the amount of bone maturation and skeletal development (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE, and WARNINGS). Palliation of inoperable mammary cancer in women: A dosage of 200 to 400 mg every 2 to 4 weeks is recommended. Women with metastatic breast carcinoma must be followed closely because androgen therapy occasionally appears to accelerate the disease. CONTRAINDICATIONS: This preparation is also contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of its components. WARNINGS: Prolonged use of high doses of androgens has been associated with the development of peliosis hepatis and hepatic neoplasms including hepatocellular carcinoma (see PRECAUTIONS, Carcinogenesis). Peliosis hepatis can be a life-threatening or fatal complication. If cholestatic hepatitis with jaundice appears or if liver function tests become abnormal, the androgen should be discontinued and the etiology should be determined. Drug-induced jaundice is reversible when the medication is discontinued. Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk for the development of prostatic hypertrophy and prostatic carcinoma. Due to sodium and water retention, edema with or without congestive heart failure may be a serious complication in patients with preexisting cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease. In addition to discontinuation of the drug, diuretic therapy may be required. If the administration of testosterone enanthate is restarted, a lower dose should be used. Gynecomastia frequently develops and occasionally persists in patients being treated for hypogonadism. Androgen therapy should be used cautiously in healthy males with delayed puberty. The effect on bone maturation should be monitored by assessing bone age of the wrist and hand every six months. In children, androgen treatment may accelerate bone maturation without producing compensatory gain in linear growth. This adverse effect may result in compromised adult stature. The younger the child the greater the risk of compromising final mature height. PRECAUTIONS Because androgens may alter serum cholesterol concentration, caution should be used when administering these drugs to patients with a history of myocardial infarction or coronary artery disease. Serial determinations of serum cholesterol should be made and therapy adjusted accordingly. A causal relationship between myocardial infarction and hypercholesterolemia has not been established. Information for Patients The physician should instruct patients to report any of the following side effects of androgens: Geriatric Use Drug/Laboratory Test Interferences Carcinogenesis There are rare reports of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients receiving long-term therapy with androgens in high doses. Withdrawal of the drugs did not lead to regression of the tumors in all cases. Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk for the development of prostatic hypertrophy and prostatic carcinoma. DRUG INTERACTIONS:
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: STORAGE SOURCE: Manufactured by: Revised: July 2007 |
Depo-testosterone (testosterone cypionate) injection
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE: DEPO-Testosterone Injection is indicated for replacement therapy in the male in conditions associated with symptoms of deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone. 1. Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)-testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome; or orchidectomy. 2. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)-idiopathic gonadotropin or LHRH deficiency, or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: It should not be given intravenously. Intramuscular injections should be given deep in the gluteal muscle. The suggested dosage for DEPO-Testosterone Injection varies depending on the age, sex, and diagnosis of the individual patient. Dosage is adjusted according to the patient's response and the appearance of adverse reactions. Various dosage regimens have been used to induce pubertal changes in hypogonadal males; some experts have advocated lower dosages initially, gradually increasing the dose as puberty progresses, with or without a decrease to maintenance levels. Other experts emphasize that higher dosages are needed to induce pubertal changes and lower dosages can be used for maintenance after puberty. The chronological and skeletal ages must be taken into consideration, both in determining the initial dose and in adjusting the dose. For replacement in the hypogonadal male, 50-400 mg should be administered every two to four weeks. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Warming and shaking the vial should redissolve any crystals that may have formed during storage at temperatures lower than recommended. CONTRAINDICATIONS:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: Prolonged use of high doses of androgens (principally the 17-a alkyl-androgens) has been associated with development of hepatic adenomas, hepatocellular carcinoma, and peliosis hepatis —all potentially life-threatening complications. Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk of developing prostatic hypertrophy and prostatic carcinoma although conclusive evidence to support this concept is lacking. Edema, with or without congestive heart failure, may be a serious complication in patients with pre-existing cardiac, renal or hepatic disease. Gynecomastia may develop and occasionally persists in patients being treated for hypogonadism. This product contains benzyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol has been reported to be associated with a fatal "Gasping Syndrome" in premature infants. Androgen therapy should be used cautiously in healthy males with delayed puberty. The effect on bone maturation should be monitored by assessing bone age of the wrist and hand every 6 months. In children, androgen treatment may accelerate bone maturation without producing compensatory gain in linear growth. This adverse effect may result in compromised adult stature. The younger the child the greater the risk of compromising final mature height. This drug has not been shown to be safe and effective for the enhancement of athletic performance. Because of the potential risk of serious adverse health effects, this drug should not be used for such purpose. PRECAUTIONS Testosterone cypionate should not be used interchangeably with testosterone propionate because of differences in duration of action. Testosterone cypionate is not for intravenous use. Information for patients Laboratory tests Serum cholesterol may increase during androgen therapy. Drug interactions Concurrent administration of oxyphenbutazone and androgens may result in elevated serum levels of oxyphenbutazone. In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may decrease blood glucose and, therefore, insulin requirements. Drug/Laboratory test Interferences Carcinogenesis Human data Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk of developing prostatic hypertrophy and prostatic carcinoma although conclusive evidence to support this concept is lacking. Pregnancy Nursing mothers Pediatric use ADVERSE REACTIONS: Endocrine and urogenital: Gynecomastia and excessive frequency and duration of penile erections. Oligospermia may occur at high dosages. Skin and appendages: Hirsutism, male pattern of baldness, seborrhea, and acne. Fluid and electrolyte disturbances: Retention of sodium, chloride, water, potassium, calcium, and inorganic phosphates. Gastrointestinal: Nausea, cholestatic jaundice, alterations in liver function tests, rarely hepatocellular neoplasms and peliosis hepatis (see WARNINGS). Hematologic: Suppression of clotting factors II, V, VII, and X, bleeding in patients on concomitant anticoagulant therapy, and polycythemia. Nervous system: Increased or decreased libido, headache, anxiety, depression, and generalized paresthesia. Allergic: Hypersensitivity, including skin manifestations and anaphylactoid reactions. Miscellaneous: Inflammation and pain at the site of intramuscular injection. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Each mL of the 100 mg/mL solution contains: Each mL of the 200 mg/mL solution contains: DEPO-Testosterone Injection is available as follows: SOURCE: |
First®- testosterone / and testosterone mc
| FIRST®- Testosterone / and Testosterone MC FIRST®- Testosterone FOR PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING ONLY DESCRIPTION Each FIRST®- Testosterone in White Petrolatum Compounding Kit contains 1.4312 grams of micronized testosterone propionate USP (100 mg testosterone per mL) in solution* (total volume: 12 mL) with sesame oil NF, butylated hydroxytoluene NF, and benzyl alcohol NF. FIRST®- Testosterone in White Petrolatum Compounding Kit also contains 48 grams of white petrolatum for topical use. When compounded, the final product provides an homogeneous formulation How Supplied and Compounding Directions 1. FIRST®- Testosterone in White Petrolatum Compounding Kit contains pre-weighed white petrolatum in a mixing jar, premeasured testosterone solution, and a stirrer. 2. Important - Prior to dispensing, pour the entire contents of the bottle containing testosterone propionate in oil into white petrolatum. 3. Stir gently until homogeneous in appearance (2 to 3 minutes). Prior to compounding, store FIRST®- Testosterone in White Petrolatum Compounding Kit at room temperature between 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). Also store final formulation at room temperature, 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). FIRST®- Testosterone in White Petrolatum Compounding Kit components have a three-year expiration date.** Based on real time controlled room temperature and humidity testing, FIRST®- Testosterone MC DESCRIPTION How Supplied and Compounding Directions 1. Testosterone MC in Moisturizing Cream Base Compounding Kit contains pre-weighed moisturizing cream base in a mixing jar, pre-measured testosterone solution, and a stirrer. 2. Important - Be careful not to spill the contents while mixing. Prior to dispensing, pour a few drops of the testosterone propionate in oil into moisturizing cream base. 3. Mix well to wet the base. 4. Continue to gradually add testosterone propionate in oil into moisturizing cream base and mix until all of the testosterone propionate in oil has been added to the moisturizing cream base 5 Continue stirring until homogeneous in appearance (2 to 3 minutes). SOURCE: |
Fortesta® (testosterone) gel for topical use
INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) Important limitations of use: Safety and efficacy of FORTESTA in males <18 years old have not been established DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
ADVERSE REACTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS:
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS: Review PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: SOURCE: © 2012 Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved. |
Striant® (testosterone buccal system)
| DESCRIPTION Striant® (testosterone buccal system) is designed to adhere to the gum or inner cheek. It provides a controlled and sustained release of testosterone through the buccal mucosa as the buccal system gradually hydrates. Insertion of Striant® twice a day, in the morning and in the evening, provides continuous systemic delivery of testosterone. Striant® is a white to off-white colored, monoconvex, tablet-like, mucoadhesive buccal system. Striant® adheres to the gum tissue above the incisors, with the flat surface facing the cheek mucosa. The active ingredient in Striant® is testosterone. Each buccal system contains 30 mg of testosterone. Testosterone USP is practically white crystalline powder chemically described as 17-beta hydroxyandrost-4-en-3one. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchidectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone levels and gonadotropins (FSH, LH) above the normal range. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) -- idiopathic gonadotropin or LHRH deficiency, or pituitary hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These patients have low serum testosterone levels but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range. ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Upon opening the packet, the rounded side surface of the buccal system should be placed against the gum and held firmly in place with a finger over the lip and against the product for 30 seconds to ensure adhesion. Striant® is designed to stay in position until removed. If the buccal system fails to properly adhere to the gum or should fall off during the 12-hour dosing interval, the old buccal system should be removed and a new one applied. If the buccal system falls out of position within 4 hours prior to the next dose, a new buccal system should be applied and it may remain in place until the time of next regularly scheduled dosing. Patients should take care to avoid dislodging the buccal system. Patients should check to see if Striant® is in place following toothbrushing, use of mouthwash and consumption of food or alcoholic/non-alcoholic beverages. Striant® should not be chewed or swallowed. To remove Striant®, gently slide it downwards from the gum towards the tooth to avoid scratching the gum. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Striant® is not indicated for use in women, and must not be used in women. Testosterone supplements may cause fetal harm. Striant® should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients, including testosterone USP that is chemically synthesized from soy. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
PRECAUTIONS: General Too frequent or persistent erections of the penis. Information for Patients Advise patients to regularly inspect the gum region where they apply Striant® and to report any abnormality to their health care professional. Laboratory Tests Drug interactions Insulin Corticosteroids Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility Human data Striant® has been evaluated in patients for 1 year without reports of cancer related to the product. However, safety in patients beyond 1 year has not been established. Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk for the development of prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma. Geriatric patients and other patients with clinical or demographic characteristics that are recognized to be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer should be evaluated for the presence of prostate cancer prior to initiation of testosterone replacement therapy. In men receiving testosterone replacement therapy, surveillance for prostate cancer should be consistent with current practices for eugonadal men. Pregnancy Category X Teratogenic Effects Labor and Delivery Nursing Mothers Pediatric Use Geriatric Use DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: Striant® is supplied in transparent blister packs containing 10 doses. It is white to off- white colored with a flat edge on one side and a convex surface on the other. Each Striant® buccal system contains 30 mg of testosterone and is supplied as follows: SOURCE: |
Testim® (testosterone gel)
| DESCRIPTION Testim® (testosterone gel) is a clear to translucent hydroalcoholic topical gel containing 1% testosterone. Testim® provides continuous transdermal delivery of testosterone for 24 hours, following a single application to intact, clean, dry skin of the shoulders and upper arms. One 5 g or two 5 g tubes of Testim® contains 50 mg or 100 mg of testosterone, respectively, to be applied daily to the skin’s surface. Approximately 10% of the applied testosterone dose is absorbed across skin of average permeability during a 24-hour period. The active pharmacological ingredient in Testim® is testosterone. INDICATIONS AND USAGE: 1] Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone levels and gonadotropins (FSH, LH) above the normal range. 2] Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): idiopathic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum levels but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range. Testim® has not been clinically evaluated in males under 18 years of age. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Upon opening the tube the entire contents should be squeezed into the palm of the hand and immediately applied to the shoulders and/or upper arms (area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by the patient’s short sleeve t-shirt). Application sites should be allowed to dry for a few minutes prior to dressing. Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap and water after Testim® has been applied. In order to prevent transfer to another person, clothing should be worn to cover the application sites. If direct skin-to-skin contact with another person is anticipated, the application sites must be washed thoroughly with soap and water. In order to maintain serum testosterone levels in the normal range, the sites of application should not be washed for at least two hours after application of Testim®. Do not apply Testim® to the genitals or to the abdomen. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Pregnant and nursing women should avoid skin contact with Testim® application sites on men. Testosterone may cause fetal harm. Testosterone exposure during pregnancy has been reported to be associated with fetal abnormalities. In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which Testim® has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of a pregnant or nursing woman, the general area of contact on the woman should be immediately washed with soap and water. Testim® should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients, including testosterone USP that is chemically synthesized from soy. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: SOURCE: Rev: September 2009 |
Testopel® pellets (testosterone)
| DESCRIPTION Testopel® Pellets (testosterone) are cylindrically shaped pellets 3.2mm (1/8 inch) in diameter and approximately 8-9mm in length. Each sterile pellet weighs approximately 77mg (75mg testosterone) and is ready for implantation. Androgens are steroids that develop and maintain primary and secondary male sex characteristics. Testosterone is a member of this class. INDICATIONS AND USAGE: 1] Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion,orchitis, vanishing testes syndrome; or orchidectomy. 2] Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - idiopathic or gonadotropic LHRH deficiency,or pituitary - hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma or radiation. If the above conditions occur prior to puberty, androgen replacement therapy will be needed during the adolescent years for development of secondary sex characteristics. Prolonged androgen treatment will be required to maintain sexual characteristics in these and other males who develop testosterone deficiency after puberty. 1] Androgens may be used to stimulate puberty in carefully selected males with clearly delayed puberty. These patients usually have a familial pattern of delayed puberty that is not secondary to a pathological disorder; puberty is expected to occur spontaneously at a relatively late date. Brief treatment with conservative doses may occasionally be justified in these patients if they do not respond to psychological support. The potential adverse effect on bone maturation should be discussed with the patient and parents prior to androgen administration. An X-ray of the hand and wrist to determine bone age should be taken every 6 months to assess the effect of treatment on epiphyseal centers (see package insert for WARNINGS). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Dosages in delayed puberty generally are in the lower range of that listed above and, for a limited duration, for example 4 to 6 months. The number of pellets to be implanted depends upon the minimal daily requirements of testosterone propionate determined by a gradual reduction of the amount administered parenterally. The usual dosage is as follows: implant two 75mg pellets for each 25mg testosterone propionate required weekly. Thus when a patient requires injections of 75mg per week, it is usually necessary to implant 450mg (6 pellets). With injections of 50mg per week, implantation of 300mg (4 pellets) may suffice for approximately three months. With lower requirements by injection, correspondingly lower amounts may be implanted. It has been found that approximately one-third of the material is absorbed in the first month, one-fourth in the second month and one-sixth in the third month. Adequate effect of the pellets ordinarily continues for three to four months, sometimes as long as six months. CONTRAINDICATIONS: WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS: SOURCE: |
Reference(s)
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine, DailyMed Database.
Provides access to the latest drug monographs submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Please review the latest applicable package insert for additional information and possible updates. A local search option of this data can be found here.