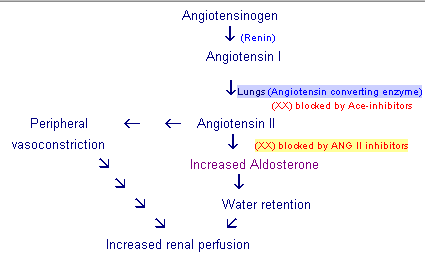
Ace Inhibitors
Benazepril (lotensin ®)
| Hypertension: Start: 10 mg/day in patients not receiving a diuretic; 20-40 mg/day as a single dose or 2 divided doses; the need for twice-daily dosing should be assessed by monitoring peak (2-6 hours after dosing) and trough responses.
Note: Patients taking diuretics should have them discontinued 2-3 days prior to starting benazepril. If they cannot be discontinued, then initial dose should be 5 mg; restart after blood pressure is stabilized if needed. Maximum: 80 mg per day. |
Captopril (capoten ®)
| Dosing (Adults) Hypertension: Start: 12.5 to 25 mg 2-3 times/day; may increase by 12.5 to 25 mg/dose at 1- to 2-week intervals up to 50 mg 3 times/day. Maximum: 150 mg 3 times/day. Add diuretic before further dosage increases. CHF : Start 6.25 to 12.5 mg three times daily. Initial dose depends upon patient's fluid/electrolyte status. Target: 50 mg 3 times/day.Prevention of LV dysfunction following MI: Oral: Initial: 6.25 mg; followed by 12.5 mg 3 times/day; increase to 25 mg 3 times/day over the next few days; following by gradual increase to a goal of 50 mg tid. Acute hypertension (urgency/emergency): Oral: 12.5 to 25 mg, may repeat as needed (may be given sublingually, but no therapeutic advantage demonstrated) Renal Dosing: |
Enalapril (vasotec ®)
| Dosing (Adults) [Use lower listed initial dose in patients with hyponatremia, hypovolemia, severe congestive heart failure, decreased renal function, or in those receiving diuretics.] Hypertension: I.V. (Start): 1.25 mg/dose, given over 5 minutes every 6 hours; doses as high as 5 mg/dose every 6 hours have been tolerated for up to 36 hours. Note: If patients are concomitantly receiving diuretic therapy, begin with 0.625 mg I.V. over 5 minutes; if the effect is not adequate after 1 hour, repeat the dose and administer 1.25 mg at 6-hour intervals thereafter; if adequate, administer 0.625 mg I.V. every 6 hours. Asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction: Oral: 2.5 mg twice daily, titrated as tolerated to 20 mg/day Heart failure: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg once or twice daily (usual range: 5-40 mg/day in 2 divided doses). Titrate slowly at 1- to 2-week intervals. Target dose: 10-20 mg twice daily (ACC/AHA 2005 Heart Failure Guidelines). Renal Dosing: Hypertension: CrCl 30-80 mL/minute: Oral: Administer 5 mg/day titrated upwards to maximum of 40 mg. CrCl <30 mL/minute: Oral: Administer 2.5 mg day titrated upward until blood pressure is controlled up to a maximum of 40 mg. For heart failure patients with sodium <130 mEq/L or serum creatinine >1.6 mg/dL, initiate dosage with 2.5 mg/day, increasing to twice daily as needed; increase further in increments of 2.5 mg/dose at >4-day intervals to a maximum daily dose of 40 mg. I.V.: CrCl >30 mL/minute: Initiate with 1.25 mg every 6 hours and increase dose based on response. CrCl <30 mL/minute: Initiate with 0.625 mg every 6 hours and increase dose based on response. Drug UPDATES: EPANED ® (enalapril maleate) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 2016 INDICATIONS AND USAGE: •treatment of hypertension in adults and children older than one month, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. ( 1.1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Heart Failure: Initiate at 2.5 mg twice daily. Titrate up to 20 mg twice daily as tolerated. Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Initiate at 2.5 mg twice daily. Titrate up to 10 mg twice daily. HOW SUPPLIED: |
Fosinopril (monopril ®)
| Dosing (Adults): Hypertension: Start 10 mg orally once a day. Maximum: 80 mg orally once daily. Most patients are maintained on 20-40 mg/day. May need to divide the dose into two if trough effect is inadequate. CHF: Start 10 mg orally once a day (5 mg if renal dysfunction present) and increase, as needed, to a maximum of 40 mg once daily over several weeks. Usual dose: 20-40 mg/day. If hypotension, orthostasis, or azotemia occurs during titration, consider decreasing concomitant diuretic dose, if any. Supplied: [10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg tabs] |
Lisinopril (prinivil ®, zestril®)
| Dosing (Adults) Hypertension: Start 10 mg orally once daily (Maintained on diuretic: Initial: 5 mg/day). Maximum: 80 mg/day.
Acute myocardial infarction (within 24 hours in hemodynamically stable patients): Oral: 5 mg immediately, then 5 mg at 24 hours, 10 mg at 48 hours, and 10 mg every day thereafter for 6 weeks. |
Moexipril (univasc ®)
| Hypertension, LV dysfunction (post MI): Start 7.5 mg once daily (in patients not receiving diuretics), 1 hour prior to a meal or 3.75 mg once daily (when combined with thiazide diuretics); maintenance dose: 7.5 to 30 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses 1 hour before meals. Maximum: 30 mg/day. Supplied : [7.5mg, 15 mg tabs] |
Perindopril (aceon ®)
| Hypertension: Start 4 mg once daily but may be titrated to response; usual range: 4-8 mg/day (may be given in 2 divided doses); increase at 1- to 2-week intervals (maximum: 16 mg/day). Concomitant therapy with diuretics: To reduce the risk of hypotension, discontinue diuretic, if possible, 2-3 days prior to initiating perindopril. If unable to stop diuretic, initiate perindopril at 2 to 4 mg/day and monitor blood pressure closely for the first 2 weeks of therapy, and after any dose adjustment of perindopril or diuretic.
Congestive heart failure: Oral: Initial: 2 mg once daily; increase at 1- to 2-week intervals; target dose: 8 to 16 mg once daily (ACC/AHA 2005 Heart Failure Guidelines) Renal Dosing: |
Quinapril (accupril ®)
| Dosing (Adults) Hypertension: Start: 10-20 mg once daily, adjust according to blood pressure response at peak and trough blood levels; initial dose may be reduced to 5 mg in patients receiving diuretic therapy if the diuretic is continued. Maximum: 80 mg/day. CHF / Post MI: Start 5 mg once or twice daily, titrated at weekly intervals to 20-40 mg daily in 2 divided doses; target dose (heart failure): 20 mg twice daily (ACC/AHA 2005 Heart Failure Guidelines). Renal Dosing: Congestive heart failure: Oral: Start: CrCl >30 mL/minute: Administer 5 mg/day. CrCl 10-30 mL/minute: Administer 2.5 mg/day. Supplied: [5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg tablets] |
Ramipril (altace ®)
| Dosing (Adults) Hypertension: Start: 2.5 mg orally once daily. Maximum: 20 mg/day. CHF: Start 1.25-2.5 mg once daily. Target dose: 10 mg once daily. Note: The dose of any concomitant diuretic should be reduced. If the diuretic cannot be discontinued, initiate therapy with 1.25 mg. After the initial dose, the patient should be monitored carefully until blood pressure has stabilized. Left ventricular dysfunction Post MI: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg twice daily titrated upward, if possible, to 5 mg twice daily. Reduce the risk of MI, stroke, and death from cardiovascular causes: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily for 1 week, then 5 mg once daily for the next 3 weeks, then increase as tolerated to 10 mg once daily (may be given as divided dose) Renal Dosing: Supplied: [1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg capsules] |
Trandolapril (mavik ®)
| Dosing (Adults): Hypertension: Start (patients not receiving a diuretic): 1 mg/day (2 mg/day in black patients). Adjust dosage according to the blood pressure response. Make dosage adjustments at intervals of 1 week. Most patients have required dosages of 2 to 4 mg/day. There is a little experience with doses >8 mg/day. Patients inadequately treated with once daily dosing at 4 mg may be treated with twice daily dosing. If blood pressure is not adequately controlled with monotherapy, a diuretic may be added. Max: 8 mg/day. CHF/post MI: Start 1 mg/day; titrate patients (as tolerated) towards the target dose of 4 mg/day. If a 4 mg dose is not tolerated, patients can continue therapy with the greatest tolerated dose. Supplied: [1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg tablets] |
Combination therapy with angiotensin ii blockers??
| "The combination of ACE-I with Angiotensin II receptor antagonists may reduce proteinuria more effectively than the two drugs alone. Moreover the addition of Statins may synergize the antiproteinuric effects of ACE-I and ATAII antagonists in experimental models of chronic renal diseases." source.
"The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is activated in several diseases, and angiotensin II mediates a number of putative detrimental effects through activation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor, while the clinical role of the type 2 receptor has not yet been settled. Inhibition of the RAS is either achieved by the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists (AIIA). Although a combined inhibitory therapy might seem attractive, thus far limited data has emerged to support such a strategy. In hypertension, losartan has proven slightly more efficient than atenolol to prevent cardiovascular complications, overall mortality was however identical. In heart failure, AIIA should only be considered in ACE inhibitor-intolerant patients. Both ACE inhibitors and AIIA have proven efficient in diabetic microalbuminuria and in proteinuria. ACE inhibitors are first-line treatment in type 1 diabetic nephropathy and in nondiabetic nephropathy, while AIIA are highly efficient in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Combination therapy might be superior to monotherapy in nondiabetic nephropathy." SOURCE: |
Prestalia ® (perindopril arginine and amlodipine
| Drug UPDATES: PRESTALIA ® (perindopril arginine and amlodipine) tablets [Drug information / PDF] Dosing: Click (+) next to Dosage and Administration section (drug info link) Initial U.S. Approval: 2015 INDICATIONS AND USAGE: In patients not adequately controlled with monotherapy . Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions (see package insert). HOW SUPPLIED: Tablets (perindopril arginine/amlodipine): 3.5/2.5 mg, 7/5 mg and 14/10 mg |
Reference(s)
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine, DailyMed Database.
Provides access to the latest drug monographs submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Please review the latest applicable package insert for additional information and possible updates. A local search option of this data can be found here.