NUZYRA ® (omadacycline) for injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Usual Diluents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NS, D5W |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Standard Dilutions [Amt of drug] [Infusion vol] [Infusion rate]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [100 mg ] [100 ml total volume] [30 minutes] [200 mg ] [100 ml total volume] [60 minutes] Reconstitution and Dilution:
Storage of the Diluted Infusion Solution The NUZYRA diluted infusion solution may be used within 12 hours at room temperature (less than or equal to 25°C) or within 7 days when refrigerated (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze. Allow the infusion bag to reach room temperature prior to use. Administration After reconstitution and dilution, administer NUZYRA by intravenous infusion, using a total infusion time of 60 minutes for a 200-mg dose, or a total infusion time of 30 minutes for a 100-mg dose |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WARNINGS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See warnings and precautions below.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DESCRIPTION OF NUZYRA
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description:
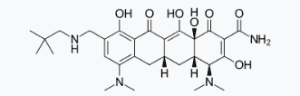 NUZYRA contains omadacycline tosylate, an aminomethylcycline which is a semisynthetic derivative of the tetracycline class of antibacterial drugs, for intravenous or oral administration. The chemical name of omadacycline tosylate is (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-(2,2-dimethylpropylaminomethyl)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide, 4-methylbenzenesulfonate. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY OF NUZYRA :
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Action:
Omadacycline is an aminomethylcycline antibacterial within the tetracycline class of antibacterial drugs. Omadacycline binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit and blocks protein synthesis. Omadacycline is active in vitro against Gram positive bacteria expressing tetracycline resistance active efflux pumps (tetK and tet L) and ribosomal protection proteins (tet M). In general, omadacycline is considered bacteriostatic; however, omadacycline has demonstrated bactericidal activity against some isolates of S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae. Resistance The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. Omadacycline was active in vitro against Gram positive bacteria that carried ribosomal protection genes (tet M) and efflux genes (tet K and tet L), and in Enterobactericeae that carried the tetB efflux gene. Additionally, omadacycline was active against some S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, and H. influenzae strains carrying macrolide resistance genes (erm A, B and/or C), or ciprofloxacin resistance genes (gyrA and parC) and beta-lactamase positive H. influenzae. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
1.1 Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP) NUZYRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) caused by the following susceptible microorganisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates), Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydophila pneumoniae. 1.2 Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI) NUZYRA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by the following susceptible microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates), Staphylococcus lugdunensis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus anginosus grp. (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), Enterococcus faecalis, Enterobacter cloacae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. 1.3 Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of NUZYRA and other antibacterial drugs, NUZYRA should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CONTRAINDICATIONS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contraindications:
NUZYRA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to omadacycline or tetracycline-class antibacterial drugs, or to any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRECAUTIONS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS: Drug information
5.1 Mortality Imbalance in Patients with Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia Mortality imbalance was observed in the CABP clinical trial with eight deaths (2%) occurring in patients treated with NUZYRA compared to four deaths (1%) in patients treated with moxifloxacin. The cause of the mortality imbalance has not been established. All deaths, in both treatment arms, occurred in patients > 65 years of age; most patients had multiple comorbidities [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. The causes of death varied and included worsening and/or complications of infection and underlying conditions. Closely monitor clinical response to therapy in CABP patients, particularly in those at higher risk for mortality [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. 5.2 Tooth Discoloration and Enamel Hypoplasia The use of NUZYRA during tooth development (last half of pregnancy, infancy, and childhood up to the age of 8 years) may cause permanent discoloration of the teeth (yellow-gray-brown). This adverse reaction is more common during long-term use of the tetracycline class drugs, but it has been observed following repeated short-term courses. Enamel hypoplasia has also been reported with tetracycline class drugs. Advise the patient of the potential risk to the fetus if NUZYRA is used during the second or third trimester of pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.4)]. 5.3 Inhibition of Bone Growth The use of NUZYRA during the second and third trimester of pregnancy, infancy and childhood up to the age of 8 years may cause reversible inhibition of bone growth. All tetracyclines form a stable calcium complex in any bone-forming tissue. A decrease in fibula growth rate has been observed in premature infants given oral tetracycline in doses of 25 mg/kg every 6 hours. This reaction was shown to be reversible when the drug was discontinued. Advise the patient of the potential risk to the fetus if NUZYRA is used during the second or third trimester of pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.4)]. 5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with NUZYRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Life-threatening hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported with other tetracycline-class antibacterial drugs. NUZYRA is structurally similar to other tetracycline-class antibacterial drugs and is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to tetracycline-class antibacterial drugs [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue NUZYRA if an allergic reaction occurs. 5.5 Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile. C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial drug treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. 5.6 Tetracycline Class Effects NUZYRA is structurally similar to tetracycline-class of antibacterial drugs and may have similar adverse reactions. Adverse reactions including photosensitivity, pseudotumor cerebri, and anti-anabolic action which has led to increased BUN, azotemia, acidosis, hyperphosphatemia, pancreatitis, and abnormal liver function tests, have been reported for other tetracycline-class antibacterial drugs, and may occur with NUZYRA. Discontinue NUZYRA if any of these adverse reactions are suspected. 5.7 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria Prescribing NUZYRA in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria [see Indications and Usage (1.3)]. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADVERSE REACTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH NUZYRA
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADVERSE REACTIONS:
See PACKAGE INSERT for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. Drug information |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
2.1 Important Administration Instructions NUZYRA for Injection: Do NOT administer NUZYRA for injection with any solution containing multivalent cations, e.g., calcium and magnesium, through the same intravenous line [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Co-infusion with other medications has not been studied [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. NUZYRA Tablets: Fast for at least 4 hours and then take with water. After oral dosing, no food or drink (except water) is to be consumed for 2 hours and no dairy products, antacids, or multivitamins for 4 hours 2.2 Dosage in Adults with Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP) For treatment of adults with CABP the recommended dosage regimen of NUZYRA is described in Table 1 below. Use NUZYRA for injection administered by intravenous infusion for the loading dose in CABP patients.
2.3 Dosage in Adults with Acute Bacterial Skin Structure and Skin Infections (ABSSSI) For treatment of adults with ABSSSI, the recommended dosage regimen of NUZYRA is described in Table 2 below. Use NUZYRA for injection administered by intravenous infusion or NUZYRA tablets orally administered for the loading dose in ABSSSI patients.
2.4 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment No dosage adjustment is warranted in patients with renal or hepatic impairment 2.5 Preparation and Administration of NUZYRA for Injection Intravenous Solution Reconstitution and Dilution:
Storage of the Diluted Infusion Solution The NUZYRA diluted infusion solution may be used within 12 hours at room temperature (less than or equal to 25°C) or within 7 days when refrigerated (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze. Allow the infusion bag to reach room temperature prior to use. Administration After reconstitution and dilution, administer NUZYRA by intravenous infusion, using a total infusion time of 60 minutes for a 200-mg dose, or a total infusion time of 30 minutes for a 100-mg dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)]. Administer NUZYRA intravenously through a dedicated line or through a Y-site. If the same intravenous line is used for sequential infusion of several drugs, the line should be flushed with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, before and after infusion of NUZYRA. The compatibility of NUZYRA with other drugs and infusion solutions other than 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP has not been established. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HOW SUPPLIED
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS:
3.1 NUZYRA for Injection Each single-dose vial contains 100 mg omadacycline (equivalent to 131 mg omadacycline tosylate) which must be reconstituted and further diluted prior to intravenous infusion. The lyophilized powder is a yellow to dark orange cake. 3.2 NUZYRA Tablets Each tablet contains 150 mg of omadacycline (equivalent to 196 mg omadacycline tosylate) in yellow, diamond-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with OMC on one side and 150 on the other side. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Storage and Stability
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16.1 How Supplied
NUZYRA for Injection NUZYRA for Injection is supplied as a sterile lyophilized powder in a single-dose colorless glass vial, with each vial containing 100 mg of NUZYRA (equivalent to 131 mg omadacycline tosylate). They are supplied as follows: 100-mg single-dose vial (NDC 71715-001-02), packaged in cartons of 10. NUZYRA Tablets NUZYRA Tablets contains 150 mg of omadacycline (equivalent to 196 mg omadacycline tosylate) in yellow, diamond-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with OMC on one side and 150 on the other side. They are supplied as follows: Blister package of 6 (NDC 71715-002-21) Unit dose blister package of 14 (NDC 71715-002-23) Unit dose blister package of 16 (NDC 71715-002-24) 16.2 Storage and Handling NUZYRA for Injection and NUZYRA Tablets should be stored at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Do not freeze. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||

