POTIGA™ (ezogabine) Tablets
(description)
| These highlights do not include all the information needed to use POTIGA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for POTIGA. POTIGA (ezogabine) Tablets Initial U.S. Approval: 2011 |
Clinical pharmacology
| Mechanism of Action The mechanism by which ezogabine exerts its therapeutic effects has not been fully elucidated. In vitro studies indicate that ezogabine enhances transmembrane potassium currents mediated by the KCNQ (Kv7.2 to 7.5) family of ion channels. By activating KCNQ channels, ezogabine is thought to stabilize the resting membrane potential and reduce brain excitability. In vitro studies suggest that ezogabine may also exert therapeutic effects through augmentation of GABA-mediated currents. Elimination: |
Indications and usage
| INDICATIONS AND USAGE POTIGA is a potassium channel opener indicated as adjunctive treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients aged 18 years and older. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in patients under 18 years of age have not been established. |
Precautions
| DRUG INTERACTIONS Ezogabine plasma levels may be reduced by concomitant administration of phenytoin or carbamazepine. An increase in dosage of POTIGA should be considered when adding phenytoin or carbamazepine. N-acetyl metabolite of ezogabine may inhibit renal clearance of digoxin, a P-glycoprotein substrate. Monitor digoxin levels. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Neuropsychiatric symptoms: Monitor for confusional state, psychotic Dizziness and somnolence: Monitor for dizziness and somnolence. QT prolongation: QT interval should be monitored in patients taking concomitant medications known to increase the QT interval or with certain heart conditions. Suicidal behavior and ideation: Monitor for suicidal thoughts or behaviors. |
Adverse reactions
| The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥4% and approximately twice placebo) are dizziness, somnolence, fatigue, confusional state, vertigo, tremor, abnormal coordination, diplopia, disturbance in attention, memory impairment, asthenia, blurred vision, gait disturbance, aphasia, dysarthria, and balance disorder. |
Dosage and administration
| DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
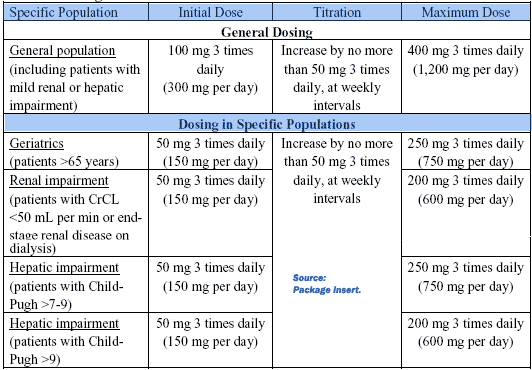
Summary: •The initial dosage should be 100 mg 3 times daily (300 mg per day) for 1 week. •Titrate to maintenance dosage by increasing the dosage at weekly intervals by no more than 150 mg per day. •Optimize effective dosage between 200 mg 3 times daily (600 mg per day) to 400 mg 3 times daily (1,200 mg per day). •When discontinuing POTIGA, reduce the dosage gradually over a period of at least 3 weeks. •Dosing adjustments are required for geriatric patients and patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment DOSING: This information is summarized in Table 1 under General Dosing. In the controlled clinical trials, 400 mg 3 times daily showed limited evidence of additional improvement in seizure reduction, but an increase in adverse events and discontinuations, compared to the 300 mg 3 times daily dosage. The safety and efficacy of doses greater than 400 mg 3 times daily (1,200 mg per day) have not been examined in controlled trials. No adjustment in dosage is required for patients with mild renal or hepatic impairment. Dosage adjustment is required in patients with moderate and greater renal or hepatic impairment. POTIGA should be given orally in 3 equally divided doses daily, with or without food. If POTIGA is discontinued, the dosage should be gradually reduced over a period of at least 3 weeks, unless safety concerns require abrupt withdrawal. Table 1: |
How supplied
| HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING POTIGA is supplied as film-coated immediate-release tablets for oral administration containing 50, 200, 300, or 400 mg of ezogabine in the following packs: 50-mg Tablets: purple, round, film-coated tablets debossed with “RTG 50” on one side in bottles of 90 (NDC 0173-0810-59). 200-mg Tablets: yellow, oblong, film-coated tablets debossed with “RTG-200” on one side in bottles of 90 (NDC 0173-0812-59). 300-mg Tablets: green, oblong, film-coated tablets debossed with “RTG-300” on one side in bottles of 90 (NDC 0173-0813-59). 400-mg Tablets: purple, oblong, film-coated tablets debossed with “RTG-400” on one side in bottles of 90 (NDC 0173-0814-59). Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] |
Reference(s)
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine, DailyMed Database.
Provides access to the latest drug monographs submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Please review the latest applicable package insert for additional information and possible updates. A local search option of this data can be found here.